Gabapentin and Alcohol Withdrawal
Can an anticonvulsant medication help with treatment for alcohol use disorder? What is the relationship between gabapentin and alcohol withdrawal? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that helps reduce and control severe epileptic seizures. Although it is not FDA approved in the treatment of alcohol use disorder, new studies have found the medication beneficial in treating alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
An estimated 30 million Americans meet the criteria for alcohol use disorder. And alcohol abuse is the 5th leading risk factor for premature death and disability worldwide. Alcohol use disorder is a chronic and relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive and heavy drinking despite negative harmful consequences. Many people who suffer from alcohol use disorder also experience alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
What is Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome?
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome can range from mild to severe and affects almost everyone who abuses alcohol. About 14% of US adults have alcohol use disorder and experience alcohol withdrawal syndrome. It usually occurs in those with long-term alcoholism who suddenly cut back on drinking or abruptly stop drinking.
The abrupt cessation of alcohol can lead to acute withdrawal syndrome within 4-12 hours after the last drink. Symptoms can persist for up to 5 days or more, depending on the severity of the alcohol use disorder.
Some of the most common side effects of alcohol withdrawal syndrome include insomnia, anxiety, tremors, seizures, hallucinations, fast heartbeat, high blood pressure and agitation.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) is a series of uncomfortable and sometimes painful side effects that occur when the body is detoxing from alcohol. Because the body has become so dependent on the substance to perform normal functions, it may have a difficult time rebalancing itself when the substance is removed. The sudden removal of alcohol from the system can send the brain and body into a chaotic fever to regain control and a baseline standard.
AWS is primarily mediated by the GABA and glutamate brain signaling in the brain. When alcohol is introduced, high levels of GABA, an inhibitory neurochemical, are released into the brain. This slows down brain activity and slows down the rest of the body. Once alcohol is removed, so are GABA neurotransmitters. They are then replaced with glutamate, which is an excitatory chemicals that quickly fire off activity in the brain. The drastic change from one end of the spectrum to another causes confusion in the body and causes symptoms of alcohol withdrawal.
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is FDA approved to treat post-herpetic neuralgia, adjunctive treatment of partial seizures, and moderate to severe restless leg syndrome. The drug was originally created as a muscle relaxer and antispasmodic medication. Brand names of the drug include Neurontin, Gralise and Horizant. Gralise is a once-daily treatment for postherpetic neuralgia and Horizant is prescribed for restless leg syndrome. The generic version has been available since 2004.
The anticonvulsant medications are thought to secondarily influence GABA and glutamate chemicals in the brain. These two neurochemicals can impact alcohol withdrawal symptoms. It can provide temporary relief and short-term relapse prevention after medical detox from alcohol.
Side effects of Gabapentin
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Issues with coordination
- Fever
- Suicidal ideation, thoughts and behaviors
- Depression and anxiety
- Withdrawal seizures
- Abnormal eye movements
- Clumsiness
- Unsteadiness
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty speaking
- Violent behavior
- Irritability
- Mania and panic attacks
- Insomnia
Check Your Insurance Coverage for FREE
Find out if your insurance covers addiction treatment in minutes. We accept most insurance!
Gabapentin and Alcohol Withdrawal
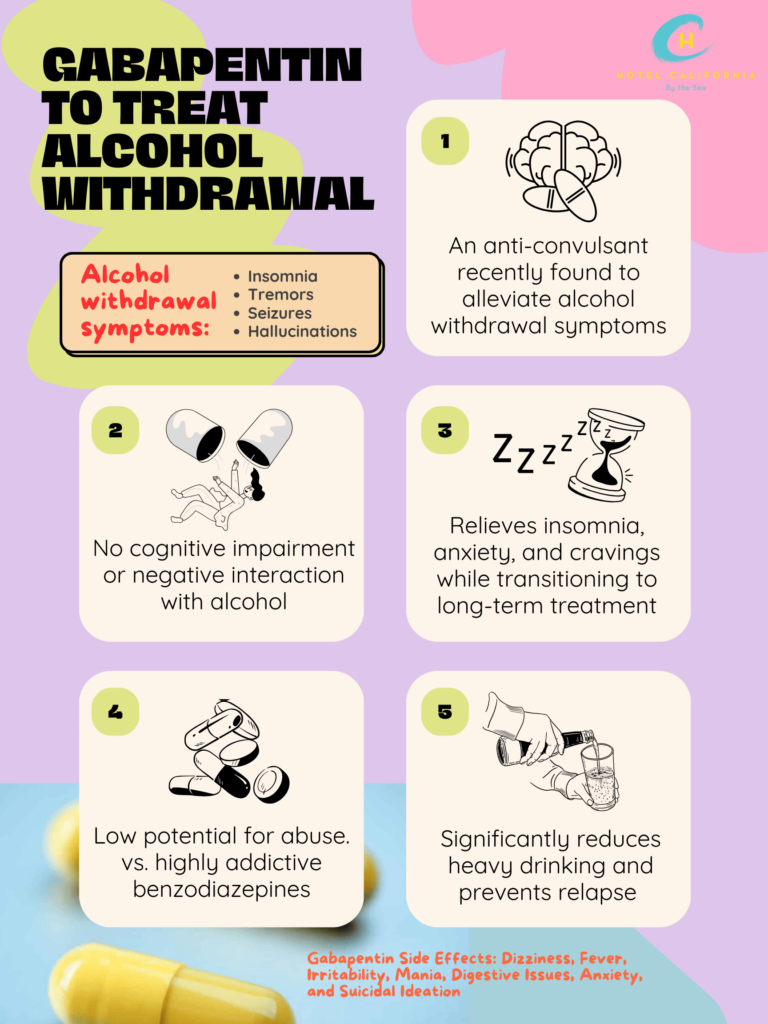
Recent studies have shown that gabapentin has had positive outcomes for relieving alcohol withdrawal symptoms. It was most effective for those with a history of more severe symptoms following the first few days of abstinence. A 2020 study found that people who took gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal symptoms tolerated the drug well and it was effective in treating the condition. In a different clinical study, gabapentin was able to promote abstinence and was effective in preventing relapse to heavy drinking.
Research has found that gabapentin can improve sleep by significantly decreasing the number of times you wake up and increasing the sleep efficiency relative to drowsiness. Gabapentin increases the concentration of GABA chemicals in the brain. It also decreases the release of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. This helps to calm down activity in the brain and body. This helps to decrease the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal like anxiety, insomnia, and cravings.
Gabapentin does not interact with alcohol because it does not impair cognition or motor control. It is not metabolized in the liver and has a low potential for abuse. This is what makes it an attractive medication for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Research finds it can be beneficial to help patients transition to longer-term types of treatment when it comes to alcohol use disorder.
While there have been many positive studies on the use of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal syndrome, it should not be used as a stand-alone treatment. The drug alone cannot support alcohol use disorder treatment, especially alcohol withdrawal seizures. It should always be used as a part of treatment care in addition to other medication-assisted treatments and cognitive therapies.
There was a study by JAMA internal medicine in March 2020, where the journal found that when gabapentin was used on patients with alcohol use disorder and alcohol withdrawal syndrome, it led to more abstinence from drinking. The study that lasted 16 weeks concluded that heavy drinking decreased and it was most effective in helping people abstain from heavy drinking and relapse.
MAT for Alcohol Use Disorder
The standard treatment for addressing alcohol withdrawal symptoms is the use of benzodiazepines. Benzos have sedative properties that slow down brain activity, which can slow down or inhibit uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms. However, benzos can also cause psychomotor impairment. This is the interruption in the connection between muscle and mental functions affecting how a person talks and walks. Patients who take benzos are also more likely to develop a tolerance, dependence and addiction to the drug.
There are three approved medications to treat alcohol use disorder: Disulfiram, Naltrexone and Acamprosate. A fourth one is called Nalmefene, but it is only approved in the European Union and is only taken as needed.
Disulfiram was first approved for the treatment of alcohol use disorder in 1951. It inhibits the enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase so that even when small amounts of alcohol are consumed, it quickly builds up with rapid onset of negative side effects like flushing, nausea and vomiting. It is often used as an alcohol deterrent.
Naltrexone is a pure opioid receptor antagonist and was approved for the treatment of alcohol use disorder back in 1994. It works by decreasing the rewarding sensation felt when drinking alcohol. Acamprosate was developed in the 1980s and approved in 2004 for the treatment of alcohol use disorder
Reach out to Hotel California by the Sea
We specialize in treating addiction and other co-occurring disorders, such as PTSD. Our Admissions specialists are available to walk you through the best options for treating your addiction.
Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder
New studies find that gabapentin can be beneficial for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome for those who suffer from alcohol use disorder. Traditionally, medications such as naltrexone and disulfiram are considered the gold standard when treating alcohol abuse. However, more clinical studies are finding that gabapentin can be a beneficial medication used as part of treatment care to help reduce heavy drinking and prevent relapse.
Hotel California by the Sea provides treatment for alcohol use disorder. We offer treatment at all levels of care including alcohol detox, residential, PHP and IOP. We utilize evidence-based treatment methods such as CBT, group therapy and family therapy. Hotel California by the Sea is dedicated to helping clients reach their goals in sobriety and overcome their addiction.
References:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2762700
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5957503
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gabapentin-and-alcohol
https://www.psychiatrist.com/pcc/gabapentin-and-withdrawal-in-alcohol-use-disorder
https://www.news-medical.net/news/20200309/How-effective-is-Gabapentin-in-alcohol-use-disorder.aspx
https://www.healthline.com/health-news/is-gabapentin-effective-treatment-for-alcohol-withdrawal-symptoms
https://www.recoveryanswers.org/research-post/can-gabapentin-help-alcohol-use-disorder-improving-sleep/