The Dangers of Mixing Ambien and Alcohol
Both Ambien and alcohol are commonly used substances among the general population around the world. Ambien is a popular prescription sleeping aid. Alcohol is a popular substance used culturally and socially. The ease of accessibility to both of these mind-altering substances means there is a higher risk of abuse, dependence and addiction. What would happen if users began mixing Ambien and alcohol?
An estimated 81 million Americans experience some sort of sleeping disorder such as trouble falling asleep, trouble staying asleep, or trouble getting a restful sleep. Sleep deprivation can become a dangerous health hazard. It can affect a person’s mood, memory, concentration, blood pressure and immune system. Sleep and rest allow the mind and body to heal and regenerate in order to keep the body system properly functioning. Good sleep is an important part of health and daily life.
Prescription sleeping aids have become popular medications used to help treat sleep conditions. When used as directed by a medical physician, they have been found to be extremely effective. However, sleeping pills such as Ambien have the potential to hinder both physical and mental health when being abused.

What is Ambien?
According to IMS Health, between 2006 and 2011, an estimated 38 million prescriptions for Ambien were written. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, about half a million Americans are abusing Ambien and other sedative drugs. Ambien is the brand name for the sleeping aid zolpidem. It is a non-benzo Z-drug that acts on the body’s central nervous system. The drug activates the neurotransmitter GABA. The sedative hypnotic works to slow down brain activity allowing for the body to relax and remain calm allowing for users to pursue a restful night’s sleep. In cases of overuse or abuse, Ambien can produce feelings of euphoria and high.
It is prescribed to treat insomnia as a short-term solution. Ambien was designed to have the same effectiveness as benzos such as Xanax, without the dangerous side effects and habit-forming properties. Manufacturers marketed the drug as a less addictive alternative to benzos. In general, it takes longer to develop an addiction to Ambien and symptoms of withdrawal are less severe compared to an addiction to benzos.
Despite being a vetted prescription medication issued by physicians, Ambien is highly potent and is a high risk for dependency and addiction. Due to its potentially addictive nature, the DEA labels Ambien as a schedule IV medication under the Controlled Substance Act. Physical dependence can develop in as little as a few weeks whether or not it is being used as prescribed. In fact, many people do not realize they have a dependence or addiction until they have stopped using the drug and find themselves unable to sleep without it.

Signs you may have an Ambien Addiction
- Refilling prescriptions more often
- Repeatedly taking larger and larger doses than recommended
- Experience drug cravings
- Engaging in dangerous situations without any memory of them later
- Spending large amounts of money on drugs
- Self-isolating away from friends, families and loved ones
Ambien is available in several different forms. Ambien, Edluar and Zolpimist are immediate-release tablets that help users who have difficulty falling asleep. Intermezzo is an extended-release formulation that is designed to help users stay asleep if they often wake up in the middle of the night and have trouble falling back to sleep. This formulation is a controlled release that allows the medication to move in the body slowly over a period of time.
Common Side Effects of Ambien include:
- Tiredness
- Poor coordination
- Daytime lethargy
- Weakness, dizziness or feeling faint
- Stuffy nose
- Dry mouth
- Irritated throat
- Headache
- Muscular pain
- Nausea and upset stomach
- Agitation
- Depression and anxiety
- Feelings of aggression
- Unusual thoughts or behaviors
- Memory impairment
- Mental confusion
- Hallucinations
- Development of unusual sleep behaviors such as sleepwalking, sleep talking and sleep eating
Ambien and Alcohol
Ambien and alcohol are both central nervous system depressant drugs and can affect the mind and body similarly. They produce side effects that relate to depression of functions in the body including lowering heart rate, lowering blood pressure and causing intense relaxation and drowsiness. Mixing Ambien and alcohol can enhance the side effects of both substances and is referred to as “potentiating.” With potentiating, the depressive effects become exponential compared to linear and withdrawal symptoms are amplified.
Amplified effects of the combination of Ambien and alcohol include the development of sleep-related disorders. Sleepwalking, sleep talking and even sleep driving have been known to happen under the influence of both substances. It can cause users to engage in dangerous behaviors without inhibitions and without memory of those events. This is because users often experience blackouts and are unable to recall any actions or behaviors that took place during the time in which they were under the influence of those substances.
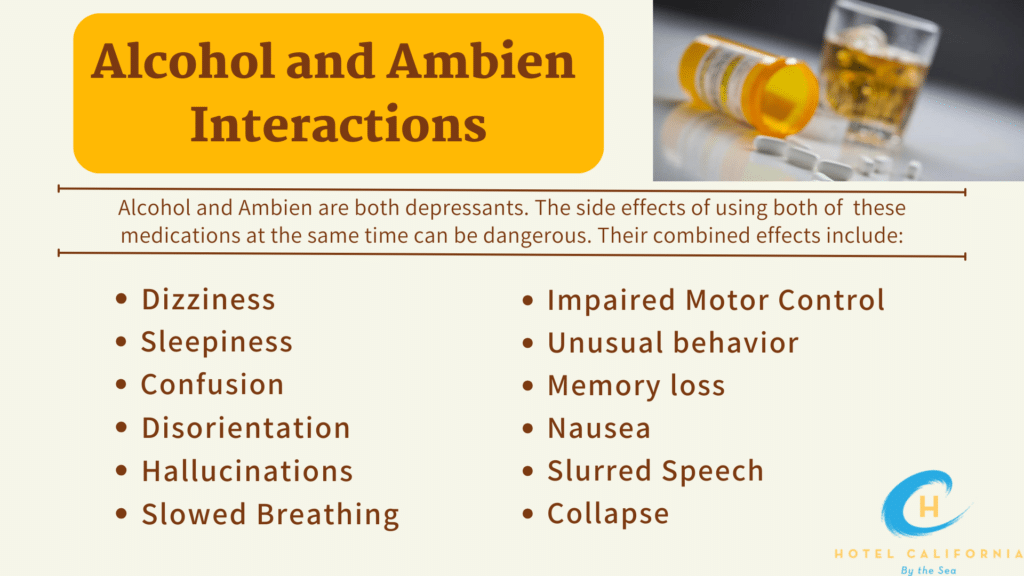
Mixing Ambien and alcohol has the potential to cause alcohol overdose and alcohol poisoning. Users can lose consciousness, develop cardiorespiratory depression or can lead to overdose. With alcohol poisoning, users will experience a lowered body temperature, mental confusion and extremely slowed breathing. In extreme cases, the user will begin vomiting, become unresponsive, develop severe dehydration and experience seizures and brain damage. When either of these two conditions occurs, it becomes dangerous and a medical emergency.
Polysubstance use can also lead to an Ambien overdose. It can cause the user to feel extreme lethargy, impaired memory and mental cognition. Some users can even experience hallucinations. Users who combine both depressant medications can also see signs of liver damage. The liver is in charge of processing and filtering out substances that enter the body. If the user is already experiencing alcohol-related liver conditions, adding Ambien on top can only cause more damage. The time in which it takes the body to eliminate Ambien properly is about 9 hours in a person with an alcohol-related liver condition. This is a drastic difference from the 2-hour processing time in a normal healthy person who does not have liver damage from alcohol use.
Mixing Ambien and alcohol raises the risk for CNS depression. Central nervous system depression can lead to confusion, lowered heart rate, seizures and abnormal breathing. The central nervous system is the command center of the brain. It tells the rest of your body how to function. It tells your lungs to breathe and your heart to beat. When the CNS is being altered or slowed down too much, it can cause life-threatening conditions.
Check Your Insurance Coverage for FREE
Find out if your insurance covers addiction treatment in minutes. We accept most insurance!
Side Effects of Ambien and Alcohol Polysubstance Use
- Dizziness and headache
- Delirium
- Drowsiness
- Inability to concentrate
- Loss of consciousness
- Slowed or slurred speech
- Overdose
- Enhanced withdrawal
- Memory loss
- Sleep disorders
- Balance issues
- Abnormal thoughts and dreams
- Heart palpitations
Addiction specialists and medical physicians highly discourage mixing Ambien and alcohol. Mixing both substances is never safe and leads to a greater risk of overdose, says Dr. Jason Kellogg, MD, Medical Director for Hotel California by the Sea. People who have a substance or alcohol use disorder generally have and can develop a higher tolerance for drugs. This often leads to an increased likelihood of dependence on other substances such as Ambien. It is possible to become addicted to both Ambien and alcohol.
The combination of the two substances actually hinders Ambien’s ability to do its job. When taking Ambien, users can experience a state of being between sleep and wakefulness. When alcohol is added to the mix, that state of in-between is extended and users find it difficult to transition into a deep and restful sleep.
Reach out to Hotel California by the Sea
We specialize in treating addiction and other co-occurring disorders, such as PTSD. Our Admissions specialists are available to walk you through the best options for treating your addiction.
Treatment for Ambien and Alcohol Addiction
Ambien and alcohol addiction can become a serious and dangerous medical condition. At Hotel California by the Sea, our prescription medication treatment program along with our alcohol use disorder treatment program are designed to help clients overcome difficult addictions. We offer varying levels of care designed to meet the needs of each client.
Intensive alcohol detox allows clients to safely remove alcohol from their bodies with the help of medication-assisted treatments overseen by experienced clinicians. Residential programs offer intensive therapies such as CBT, DBT and EMDR therapy. Addressing co-occurring mental health conditions can help clients better understand their addiction and how they can heal. Outpatient programs such as our PHP and IOP offer therapies and continuing support as our clients slowly transition into independent lives.
At Hotel California by the Sea, we believe there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to addiction treatment. Clients will receive individualized care based on their specific needs in treatment and recovery. Our behavioral health program touches on every aspect of addiction in order to help clients achieve success in sobriety and recovery.
References:
https://www.hazeldenbettyford.org/articles/ambien-and-alcohol
https://www.healthline.com/health/drugs/ambien-interactions
https://addictionresource.com/drugs/ambien/and-alcohol/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/20871-zolpidem-tablets
https://www.addictioncenter.com/sleeping-pills/ambien/
https://alcoholrehabhelp.org/interactions/ambien/